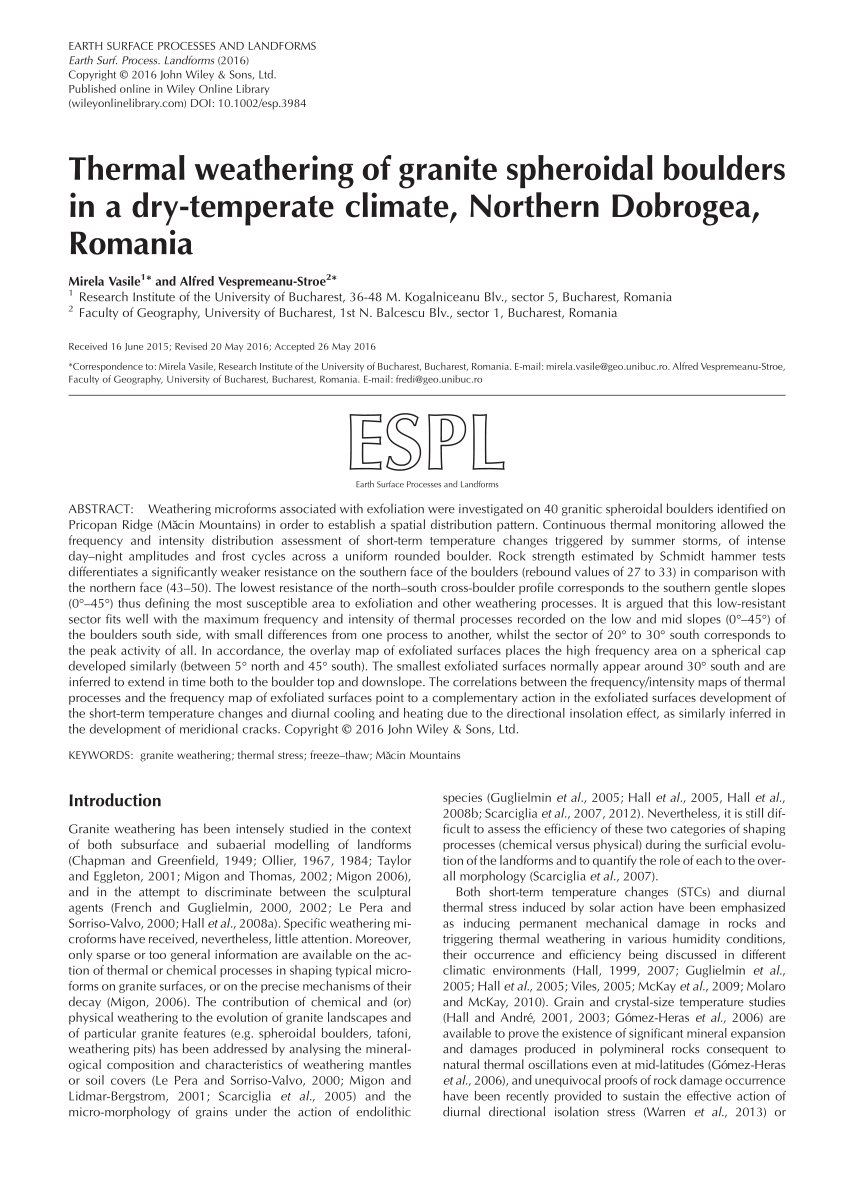
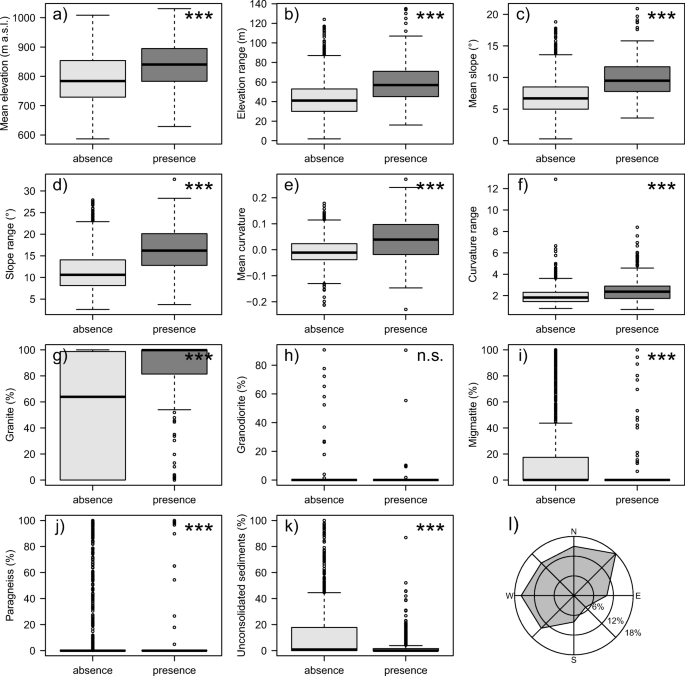
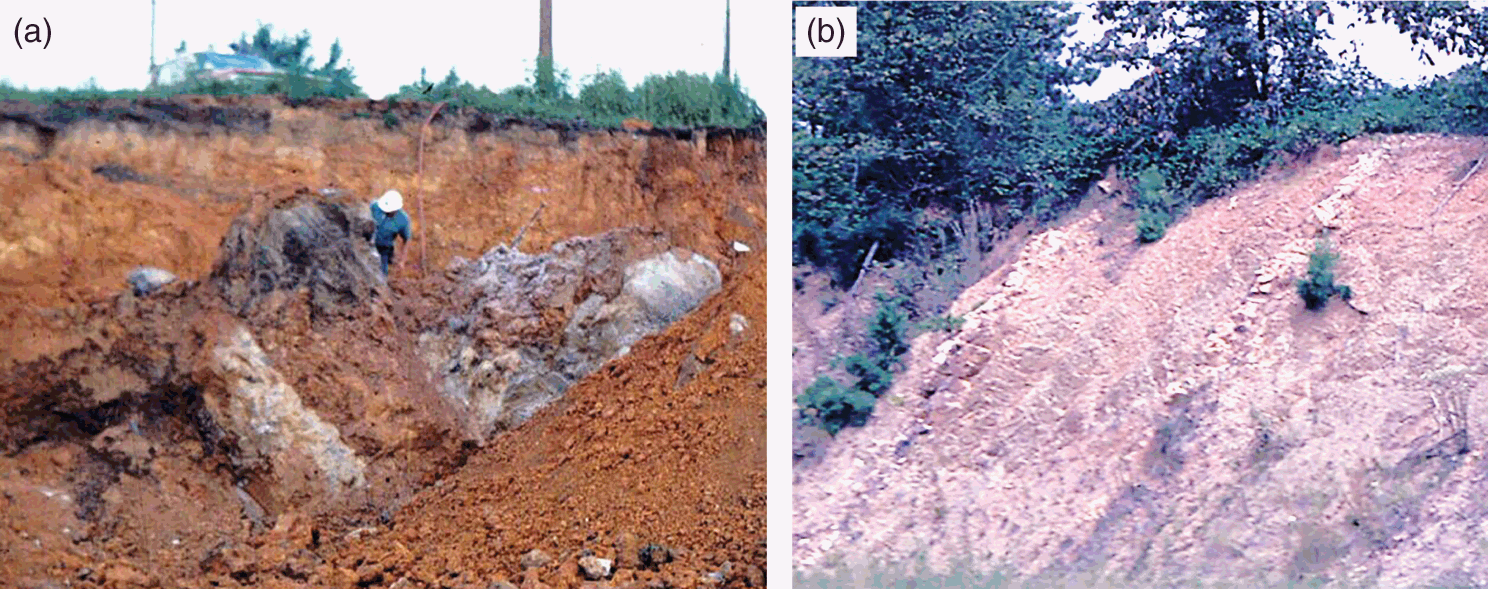
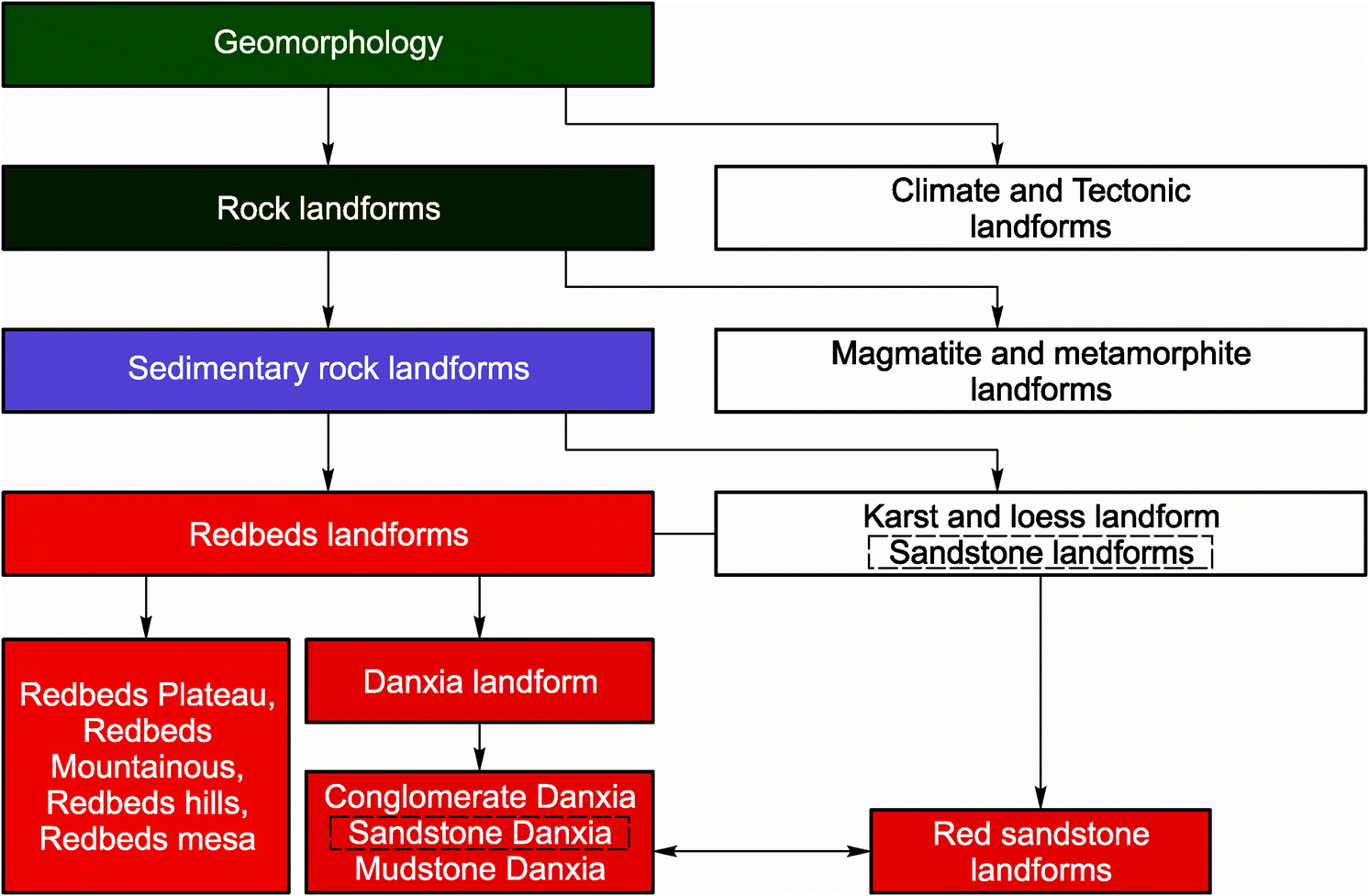
Extrusive and intrusive landforms are both formed as a result of tectonics and vulcanicity in one way or another how there is a difference between them.
Why do granite landforms vary in form and scale.
It examines granite forms and their genesis.
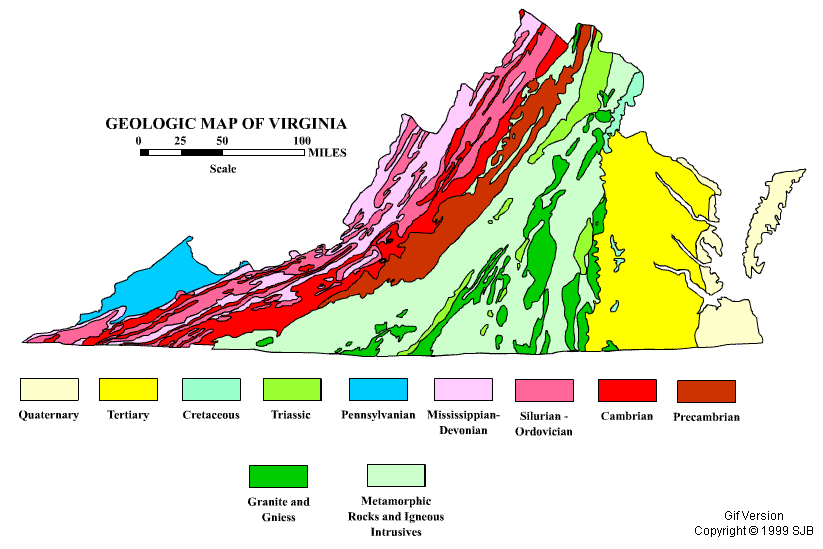
Large slabs of granite are found in areas where earth s crust is deeply eroded.
How does granite form.
This implies that a dike is always younger than the rocks that contain it.
It examines granite forms and their genesis.
The formation of granite is sparked by lava eruptions but the lava must contain the same composition as granite rhyolite which is only.
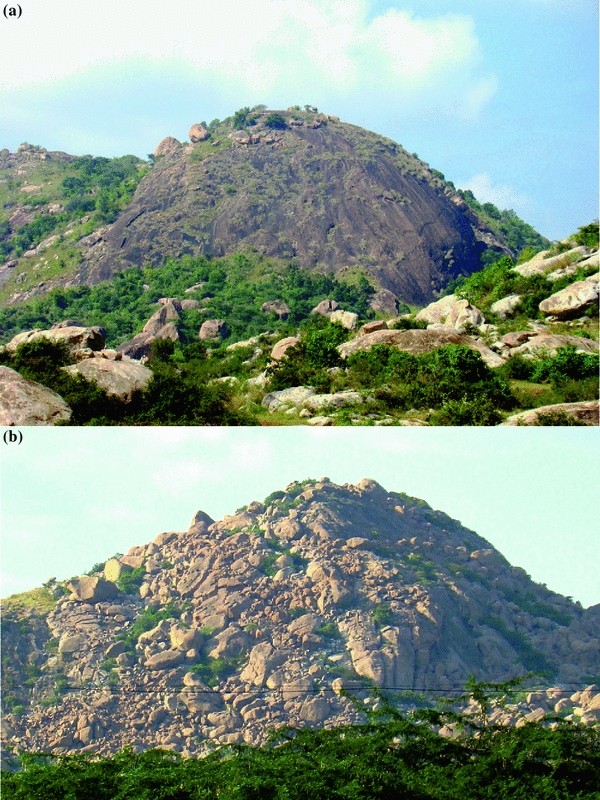
Very durable landforms as they comprise of unjointed rock cores and are virtually indestructable.
Granite landforms provides a systematic coherent and comprehensive account and analysis of granite landforms.
It is an example of an intrusive igneous rock magma cooled under the earth s crust and the granite was exposed millions of years later by erosion of the softer rocks around it to create some unique landscapes.
Formed by etchplanation theory.
And the weathering processes near the earth s surface.
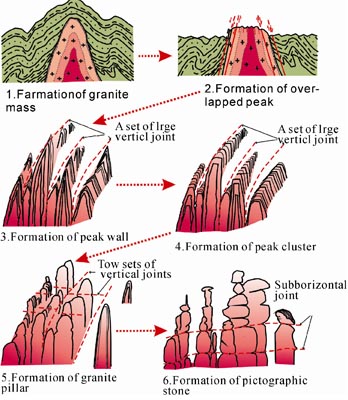
The morphology of granite exposures.
The word tectonic is derived from the greek word tekton which means.
Whereas erosion shapes landforms their origins lie in tectonic processes that build the major structures of the earth.
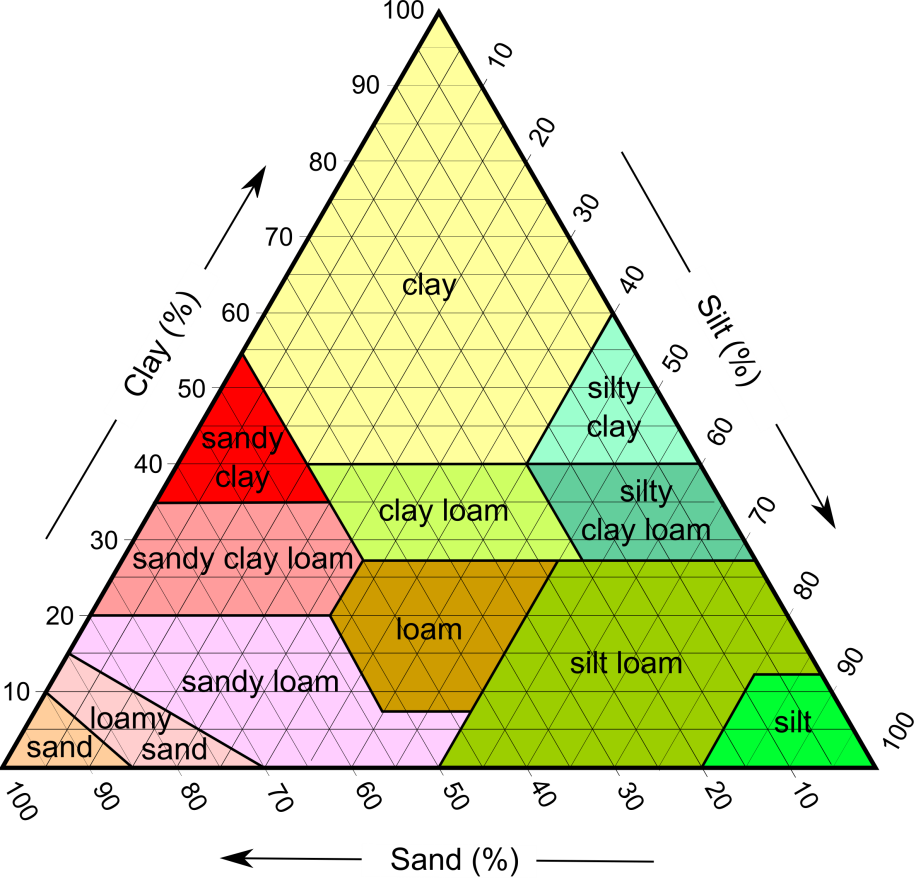
Quartz feldspar and mica.
Granite landforms provides a systematic coherent and comprehensive account and analysis of granite landforms.
Molten rock that reaches the surface to form.
And the weathering processes near the earth s surface.
A dike is an intrusion into an opening cross cutting fissure shouldering aside other pre existing layers or bodies of rock.
Granite must slowly cool in deep locations in order to produce the large grains you see throughout.
The morphology of granite exposures.
Granite landforms granite is a hard crystalline rock which is made up of three minerals.
Steep sided isolated hills that rise abruptly above the surrounding plains and show much variety in scale and morphology.
Thickness can vary from the sub centimeter scale to many meters and the lateral dimensions can extend over many kilometers.
Explain how and why extrusive volcanic landforms vary in form and scale.
The latter give rise to spectacular landscapes and include classic inventories of granite landforms such as domes inselbergs tors and minor features of selective weathering maia and nascimento.
They include mountains plateaus and rift valleys.
The nature of the materials from which granitic rocks have evolved.
Granite is an intrusive igneous rock which means it was formed in place during the cooling of molten rock generally the slower the molten rock cooled the larger it s mineral crystals with k feldspar megacrysts forming in special circumstances greater than 5cm.